Cloud native experiment with playground
1. Introduction
Typically the process to develop, build, test and deploy one vehicle applications takes months or years, at a very high cost. Due to the complexity of development process and the limitation of the development tools which are not easy and efficient to use.
On the trending of software defined vehicle, the software development process is changing. The software development process is moving from traditional waterfall model to agile model. The software development tools are moving from traditional IDE to cloud based IDE. The software development process is moving from traditional manual process to CI/CD process.
The dependency on hardware in the loop (HIL) is also changing. The HIL is moving from traditional HIL to virtual HIL. The HIL is moving from traditional hardware to cloud based hardware. The HIL is moving from traditional manual process to CI/CD process. By using the virtual HIL, the development cost time to market can be reduced significantly. To make this achievement, we need to shift more test from HIL to SIL. The SIL test is moving from traditional SIL to cloud based SIL. The SIL test is moving from traditional manual process to CI/CD process. However most the traditional SIL test run on x86 microprocessor. But the vehicle ECU/VCU is running ARM. It’s mean that, the SIL test is not running on the same architecture as the vehicle ECU/VCU. It’s not good for the SIL test. The SIL test should run on the same architecture as the vehicle ECU/VCU. The SIL test require an ARM based cloud. With the support of AWS Graviton, we can run the SIL test on ARM based cloud. The SIL test can run on the same architecture as the vehicle ECU/VCU.
Will AWS Graviton we can build an infrastructure on cloud the same as the one on vehicle. Next need a standard methodology to develop, build, test and deploy the vehicle application on cloud. This is where digital.auto and SOAFEE come in. We use digital.auto playground as an IDE to development and quickly test the app idea on web browser. We use EWAOL (an implementation of SOAFEE) to setup the infrastructure on AWS Graviton. Then we can test the app on a environment the same as the one on vehicle. Finally, we deploy again the app on dreamKIT, a hardware kit provide the full hardware stack for a vehicle to test the app with real physical signal.
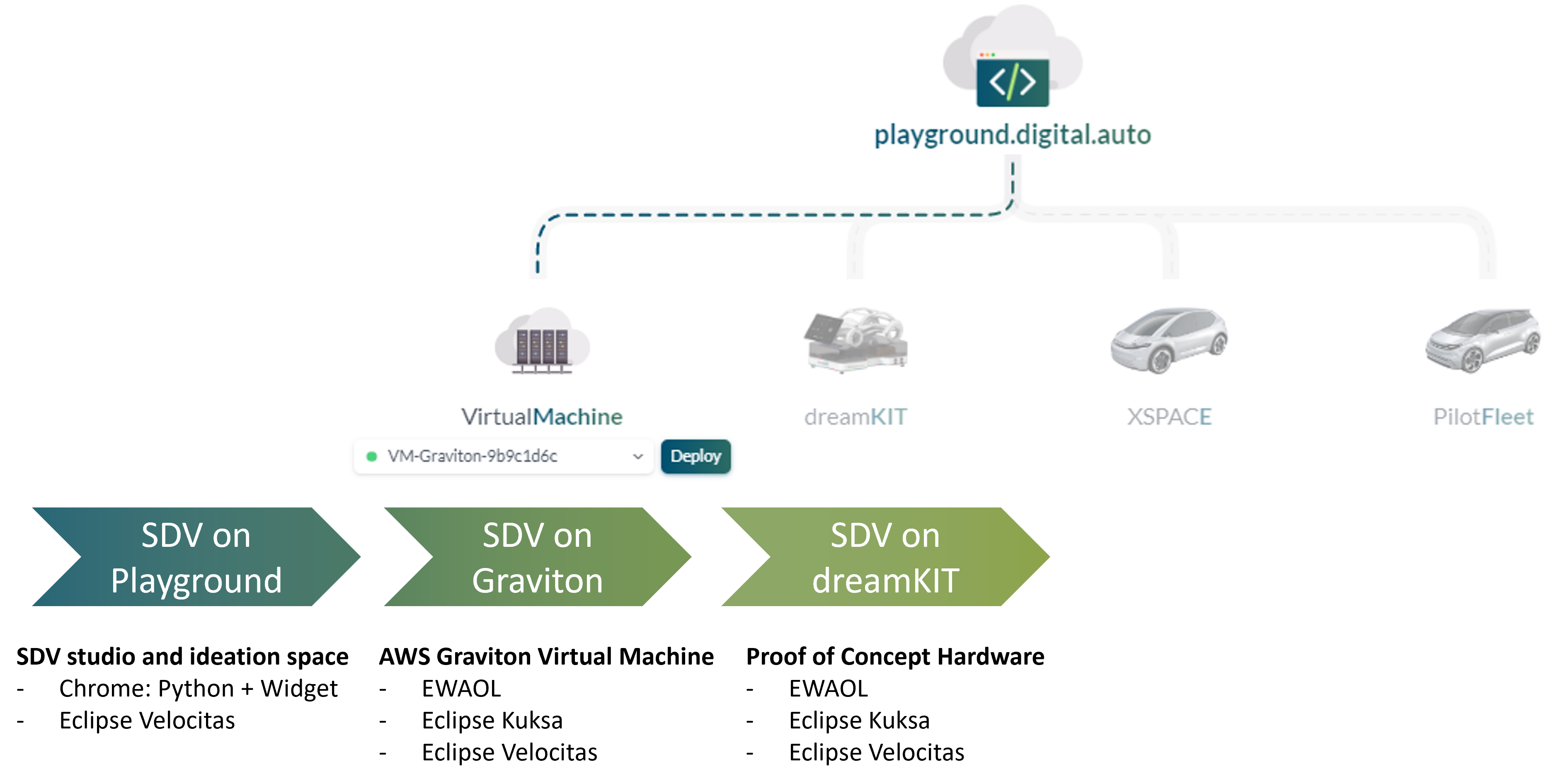
2. Setup
Because the scope of this document is only showcasing, the detail of step by step environment setup on both AWS Graviton and dreamKIT will be available outside of this page.
here is a brief view on the existing EWAOL setup on AWS Graviton at a Virtual Machine name: VM-Graviton-9b9c1d6c
Detail steps will be provided in another document.
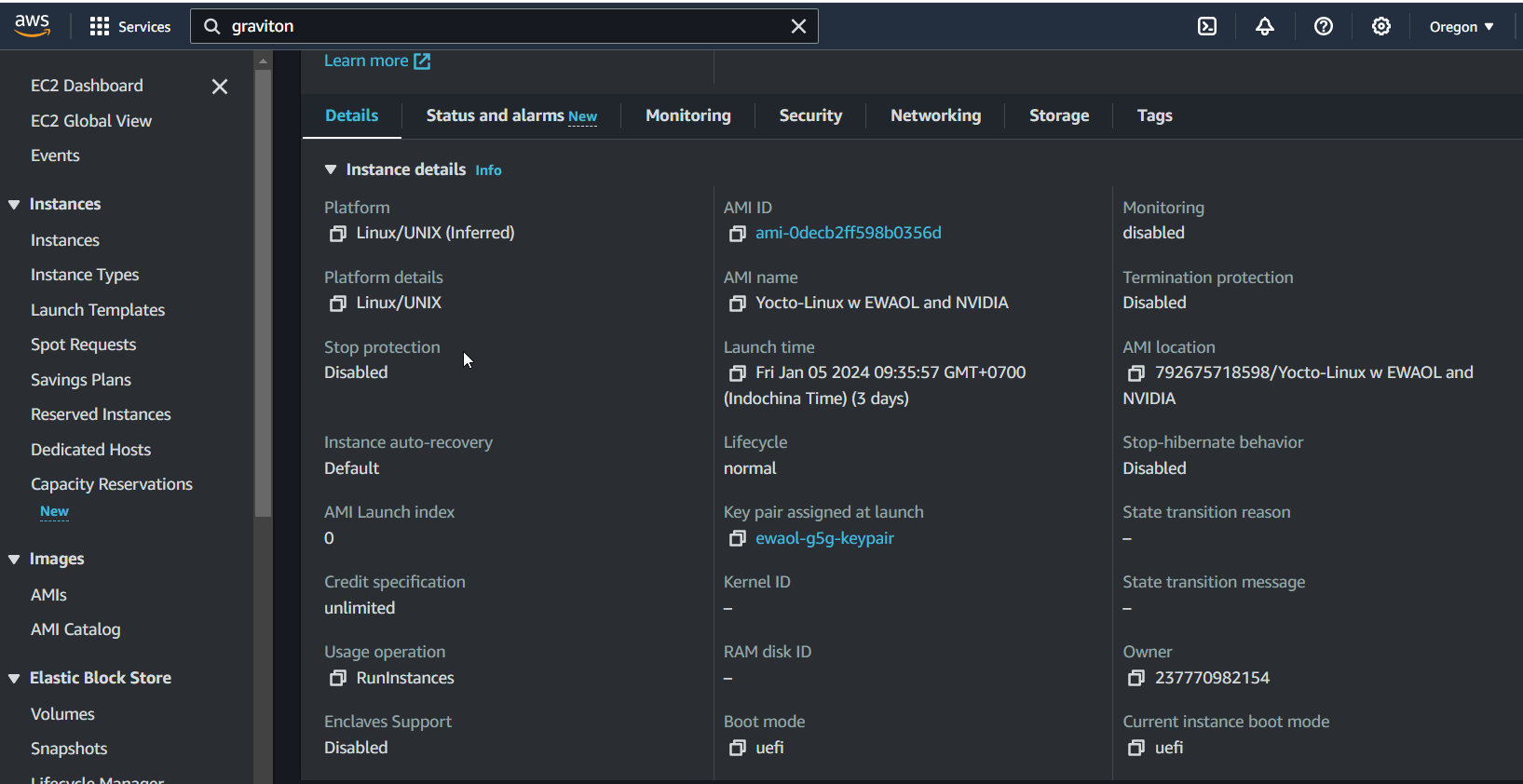
Within this VM, we have: - EWAOL: a SOAFEE implementation - docker and dapr: to run the app - Eclipse Kuksa Data Broker - Eclipse Velocitas SDK - dk-manager: a small app write in C++ to receive deploy message from digital.auto playground
3. Showcasing process
- Step 1: Write and experiment SDV app on digital.auto playground (Chrome)
- Step 2: Test sdv app on AWS Graviton
- Step 3: Test sdv app on HW PoC dreamKIT
Step 1: Write and experiment SDV app on digital.auto playground
We use digital.auto playground as an IDE to development and quickly develope and test the SdV app idea on web browser. The app is written in python follow Eclipse Velocitas Python template. By using COVESA VSS API, we can easily access the vehicle signal and control the vehicle actuator. The app is running on Chrome browser just for demonstration purpose.
digital.auto playground provide a dashboard to test the outcome of the app.
Write a simple headlight test app as below:
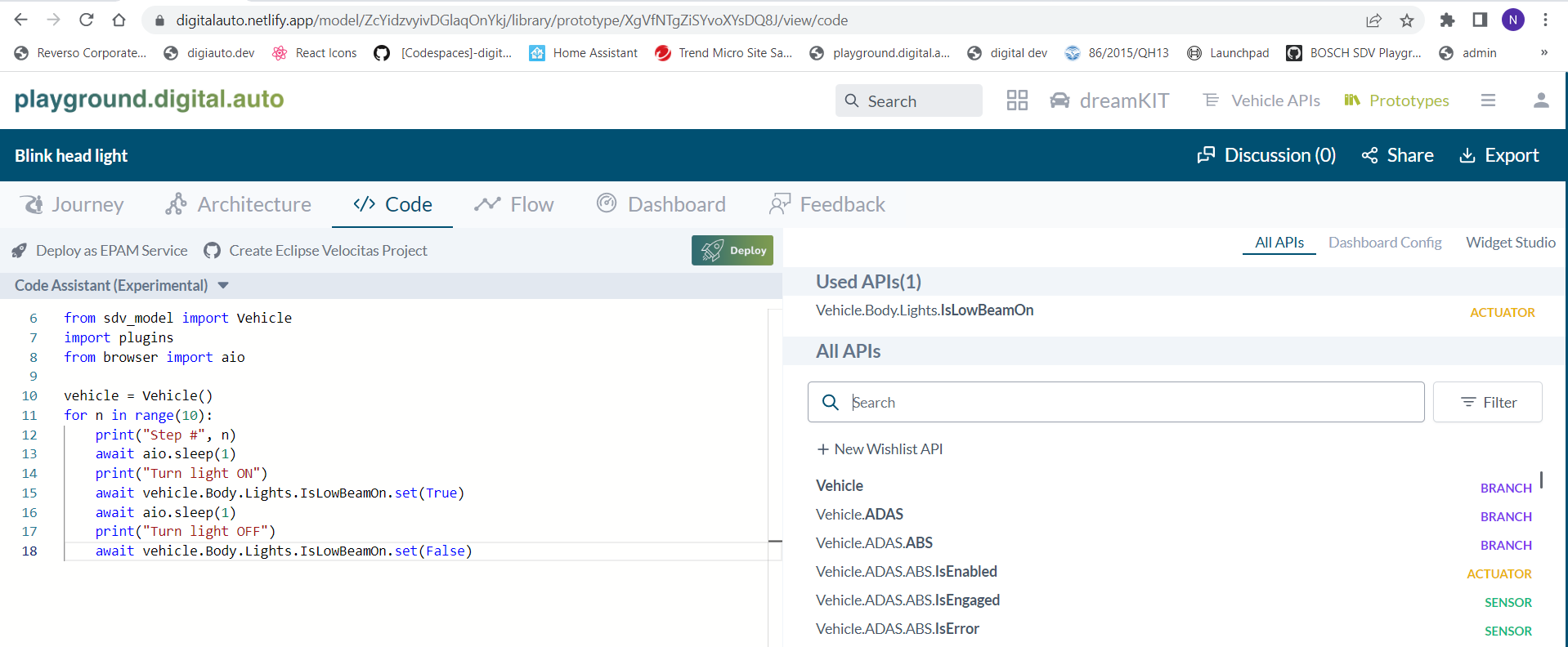
Pick a api Image-By-VSS-Value widget to test the app. The widget will show the image of the headlight status base on the API value.
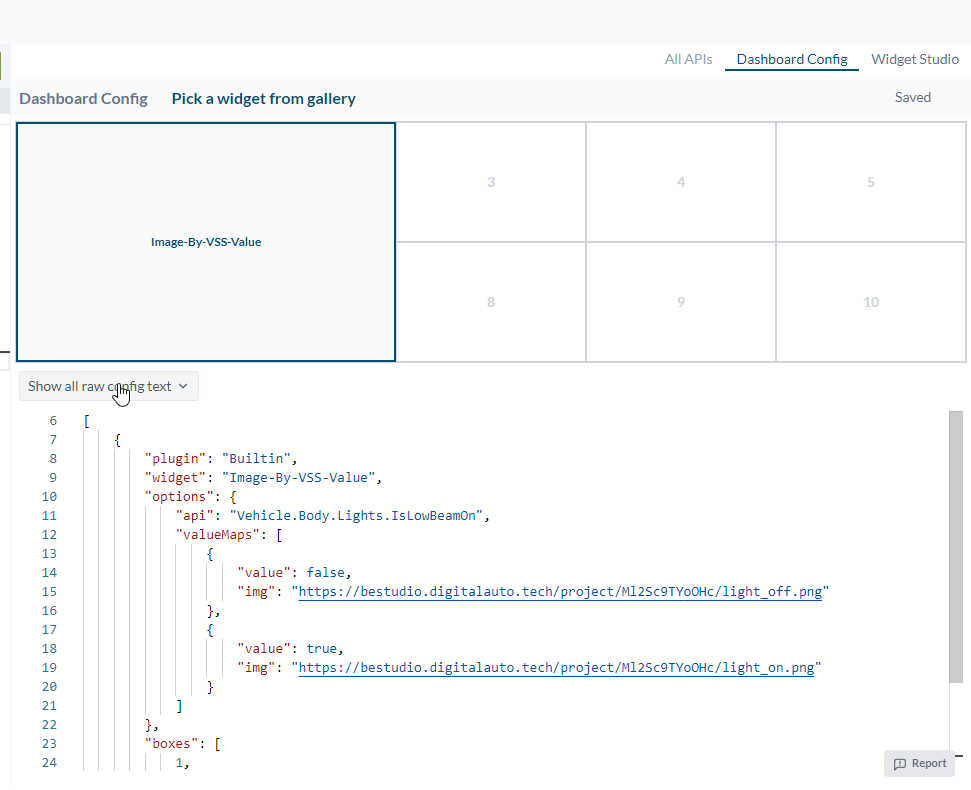
And then test the app on dashboard

The image widget and the out come form terminal show that the app is running as expect. But the test here is not fully functional test. We need to test the app on a complete vehicle environment. That’s why we need to deploy the app on EWAOL. Next, we will deploy the app on a AWS Graviton VM.
Step 2: Test sdv app on AWS Graviton
Back to the tab code, click on Deploy button. Then pick VirtualMachine icon and pick VM-Graviton-9b9c1d6c from the list. Finally, click deploy. The app will be sent to Graviton VM.
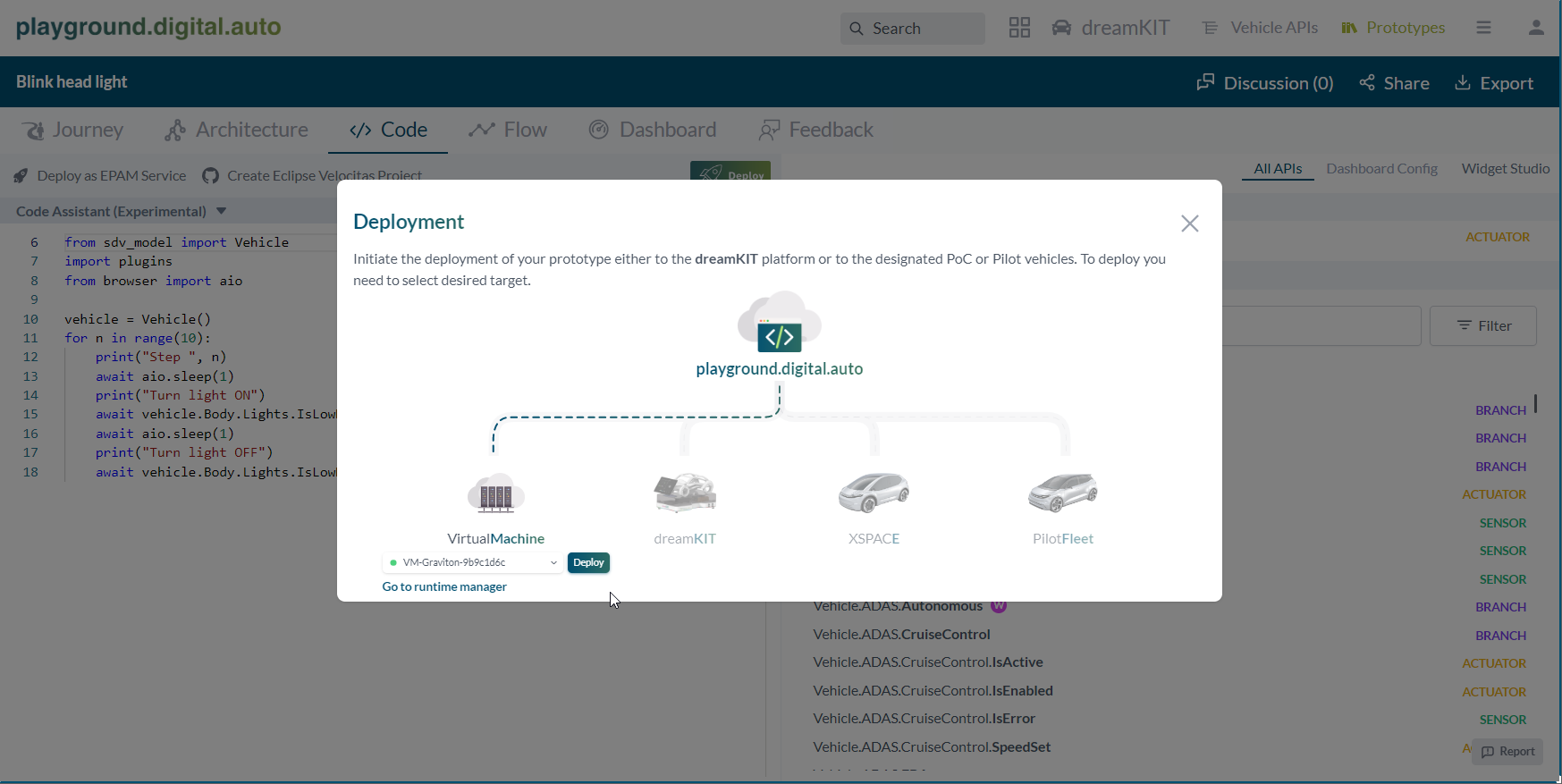
Now it time to run the app on VM. Go to runtime manager at this link: https://digitalauto.netlify.app/runtime-manager
At top right corner, pick VM-Graviton-9b9c1d6c from the target list. Then click on the app name to start the app. For this demo, we run the app name “Blink head light”. For your case, the app name is the prototype name you made on digtial.auto playground.
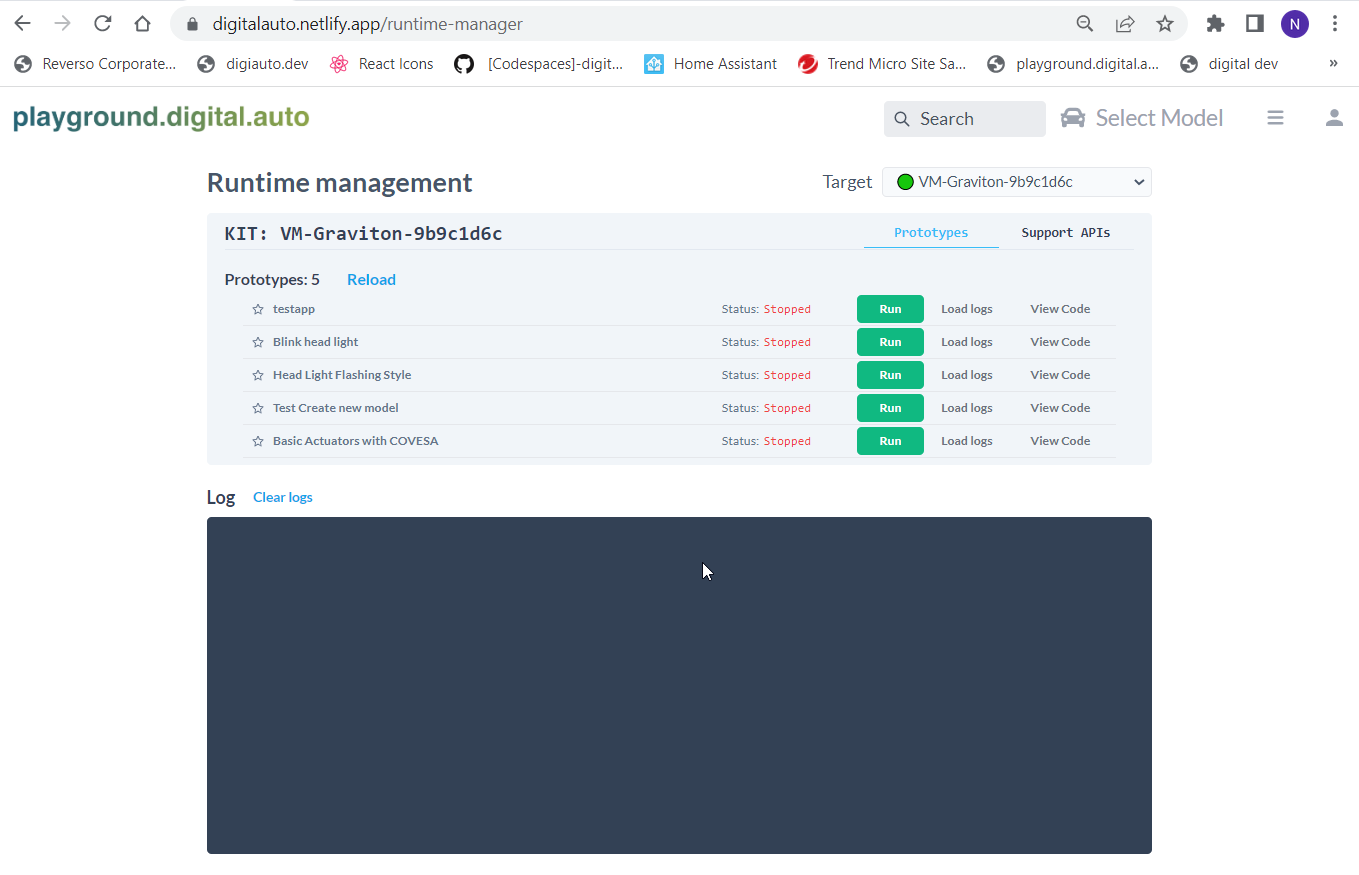
After the app is running, we can see get the log of the app by click “Load-logs” for the app you want to see the log (the one you run)
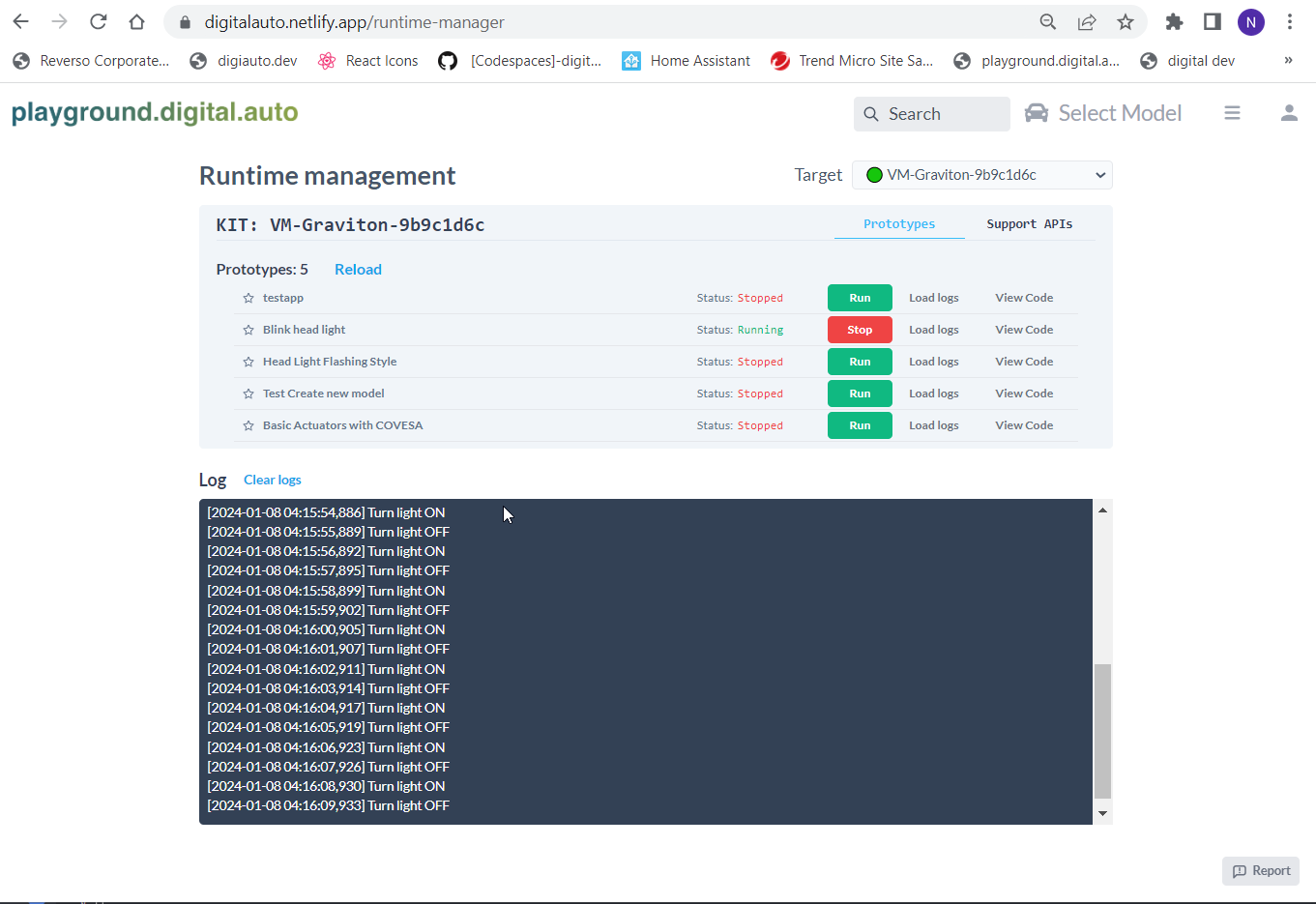
The log with the timestamp show that the app is running well on Graviton VM. Finally, we can deploy it to dreamKIT.
Step 3: Test sdv app on HW PoC dreamKIT
Same as deploy to VM, back to the tab code, click on Deploy button. Then pick dreamKIT icon and pick the dreamKIT you have from the list. Finally, click deploy. The app will be sent to dreamKIT.

From dreamKIT IVI, run the prototype you have and check that the headlight blinking as expect or not.